Have you ever felt like people are out to get you, and they have no obvious reason? Paranoia can cause one to be in a continuous panic, whereby even simple events appear threatening. It is not a matter of occasional anxieties, but it is a kind of constant belief that people are out to plan in your life, even when you have no reason to lead you to believe that. Through proper guidance, such as treatment and antipsychotic drugs, victims will be able to cope with their symptoms and improve their lives. The first step to curing paranoia is understanding that it is not alone that you face and that you need not cope with it by yourself. Stay with us till the end of the article and collect the useful information.
What Is Paranoia?
Paranoia is a condition whereby a person develops a lot of suspicion or fear, without necessarily having any cause to do so. They can assume that people are out to get them or out to attack them, even when there is no fact to back that up. This will cause even ordinary conditions to seem dangerous, and the paranoid may always feel like they are under threat, or they may not trust others.
The fear may influence their relations and life. They might find it difficult to relate to others or have faith in people in their lives. Nevertheless, it is essential to realize that paranoia is not a medical disorder but a mental health issue, and, in the conditions of proper assistance and treatment, a patient will be able to balance their emotions and enhance their state of well-being.
Paranoia Symptoms
The symptoms of paranoia are the following:
- Always being afraid that people are planning against you.
- Feeling that someone is spying on you or watching you.
- The perception of innocent remarks or actions as personal attacks.
- Isolating yourself because of the fear of betrayal or hurting.
- Tracing situations and trying to interpret them as a threat.
Dementia and Paranoia
Dementia is a disease targeting the brain that leads to loss of memory and inability to think, reason, and make accurate decisions. It may also shift the behavior and emotions of a person as they develop. Indicatively, a person suffering dementia can lose track of or forget identifiable places and people, which can provoke frustration and fear.
Dementia may occasionally result in paranoia. They may begin thinking that there is some form of conspiracy by other people to injure them or rob them, even though these thoughts are groundless. This may be highly disheartening to the individual and to the people they love. Nevertheless, the symptoms of paranoia are treatable, and the individual will feel safer and more comfortable with the proper care and attention.
Types of Paranoia
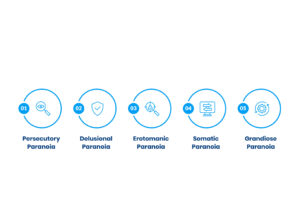
1. Persecutory Paranoia
Persecutory paranoia is a conviction that people are out to make someone sick or trick someone. Individuals who experience this form of paranoia might perceive any of their friends, family members, or even strangers as an eavesdropper or a victim. This frequently results in perpetual fear and mistrust. People may shun some areas or individuals because they feel that they are under threat. In the long run, this may drastically affect their interpersonal relations and life.
2. Delusional Paranoia
Delusional paranoia takes place when a person has strong and fixed ideas that there is an intention by others to harm them, even when there is no evidence to substantiate the idea. These assumptions have no relation to the truth and can continue even when logic or evidence of the opposite takes place. Such paranoia may result in individuals not being able to trust people who are in their circles. To some extent, they might require treatment to deal with these delusions.
3. Erotomanic Paranoia
Erotomanic paranoia involves an individual having a conviction that some other individual, mostly of high stature, is secretly after them. They might take any casual interactions as manifestations of a romantic relationship, though there is no evidence of affection or a relationship. It usually leads to emotional suffering on the part of the individual as well as the one they have a crush on. There can be treatment that includes therapy to make them understand and be able to control their thoughts.
4. Somatic Paranoia
Somatic paranoia refers to a person believing they have a severe, unknown disease/condition, whereas a medical assessment reveals no problems. It may cause people to fixate on desired medical tests or the treatment of perceived signs. They may start thinking that physicians are hiding anything or refusing to diagnose them. Such paranoia tends to lead to unnecessary medical treatment and fear of medical issues.
5. Grandiose Paranoia
Grandiose paranoia is a type of excessive self-importance, where one feels he has some special role or mission. People can believe that others are persecuting and standing in their way due to their individuality. They may also believe that the enemies or institutions are against them and do not want them to realize their objectives. It can result in risky behavior, because they can think that they are invincible or that they will become great people. There is a tendency to treat it with reality testing and assist the person to base their beliefs on reality.
Paranoia Vs Anxiety Disorders
| Paranoia | Anxiety Disorders |
| A persistent belief that others are trying to harm or deceive you. | A feeling of excessive worry or fear, often without a clear cause. |
| Suspicion, distrust, and a feeling of being targeted or persecuted. | Worry, restlessness, fear of upcoming events, and physical signs like a racing heart. |
| Fear of being betrayed or harmed by others. | Fear of specific situations, like social events or daily tasks. |
| Avoiding people or situations because of fear of betrayal. | Avoiding situations that cause distress, such as crowded places or speaking in public. |
| Medication (antipsychotics) and therapy. | Therapy (CBT) and medications like SSRIs or benzodiazepines. |
How To Help Someone with Paranoia?
When judging someone who is paranoid, one should be very tolerant and understanding. The first one is to make them feel free to speak in a stress-free and safe environment. Please do not argue with them about their beliefs because this may create more isolation or defensiveness in them. Rather than this, listen and demonstrate care.
The third step is to encourage them to take up professional assistance, including therapy or counseling. A mental health professional would assist them in investigating the cause of their paranoia and educate them on coping mechanisms. With sensitivity, please make an offer to help make appointments or get a support group, but follow through on their choice when they are not yet ready to take such a step.
What Stage Is Paranoia in Dementia?
In dementia, paranoia normally occurs in its later stages. The development of dementia may result in confusion, the loss of memory, and the inability to differentiate between reality and imagination because of the brain changes. This may make an individual paranoid about other people and assume that the people are robbing them or attempting to hurt them, yet there may be no sign to indicate this. Such paranoias are enough to complicate their day-to-day life and heighten anxiety on behalf of the individual.
But paranoia may also manifest itself earlier on, relative to the individual. It can be imperceptible initially, such as losing things and believing it is somebody else. They can become more prominent and common with the exacerbation of the dementia. Early onset of these signs is important because the caregivers can offer the required support.
How To Deal with Paranoia?
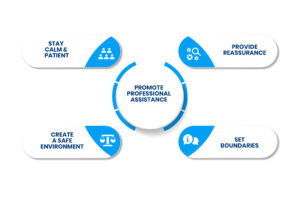
1. Stay Calm and Patient
In situations that involve paranoia, one should remain calm. Be kind and understanding, although the beliefs of the individual one deals with may appear unreasonable. You should not shout or quarrel, because it will add to their panic. Rather, be sensitive and allow them room to air out their emotions.
2. Provide Reassurance
Calm the individual down by telling them he is safe and not alone. Remind them not to worry, but do not brush their emotions off. Make them feel that you are with them and you want them to feel good and safe.
3. Promote Professional Assistance
Assure the individual to get professional help, such as therapy or counseling. A mental health professional can provide methods of coping with paranoia and discuss the underlying issues. To assist them, you can offer to make the appointments or meet them in case they are nervous to request assistance.
4. Create a Safe Environment
Attempt to minimize precipitants that may lead to paranoia. Make their environment predictable and not hectic, with familiar things and places. This can be reduced by getting rid of any stress or confusion, and this will make them more relaxed.
5. Set Boundaries
One should establish healthy boundaries as well as be supportive. In case the paranoia results in disruptive and harmful behavior, then explain amicably why there exist boundaries of what is acceptable. Help should be given, but at the same time, take care of yourself as well.
Paranoia Treatments
How to treat paranoia? So, the first way to treat paranoia is with medication, which should also be effective in case paranoia is connected with another condition, such as anxiety or schizophrenia. Also, fear and stress are minimized by establishing an environment that is safe and conducive. Constant contact with the healthcare professionals should be encouraged to keep track of progress. Last but not least, the family and friends can offer valuable emotional assistance in terms of patience and understanding.
Paranoia Test
A paranoia test typically entails having a mental health practitioner ask questions of the recipient to know what they think and feel. They can enquire about past experiences, fears, and what the individual thinks with regard to the world. The test may assist in the determination of whether the paranoia arose as a result of a larger mental health disorder. During the test, one needs to be truthful because the professional will offer the relevant support.
Medication For Paranoia
Treatment of paranoia can involve the use of antipsychotic medications, which help in the management of the symptoms by balancing the chemicals in the brain. Doctors can also prescribe it as an antidepressant or anti-anxiety medication when paranoia is associated with such conditions. When taking these drugs, it is vital to follow the prescription of a doctor. Never begin or switch a drug without consulting a physician.
Final Thoughts
We are familiar with the difficulties associated with paranoia and how it affects our day-to-day lives through MAVA Behavioral Health. Most paranoia cases may stem from some underlying mental illnesses, and paranoia has symptoms that can be painful to both individuals and those who love them.
Antipsychotics or antidepressants balance the chemicals in the brain and help manage the symptoms. It is the mission of our team to offer people caring treatment in assisting the patient to take back and enhance their living conditions. We can help you in case of paranoia, or that of someone you love.
FAQs
What is paranoia?
Paranoia is that of someone being too scared or distrustful to the point of thinking that other people are attempting to harm, deceive, or plot schemes against them without evidence to validate it.
What causes paranoia?
Mental illnesses such as schizophrenia, anxiety, or depression may cause paranoia. It may also be a trauma, stress, or substance abuse outcome.
How is paranoia treated?
The therapy may involve therapy and medications like antipsychotics, antidepressants, among others, which depend on the underlying cause of paranoia.
Can paranoia be cured?
Although paranoia cannot be treated, the treatment can control the symptoms of the condition, which enables an individual to live a more comfortable and steady life.
What do I do to assist a paranoid person?
Be tolerant, non-judgmental, and persuade them to consult professional help and provide them with a secure and conducive environment to help lessen their fears.









